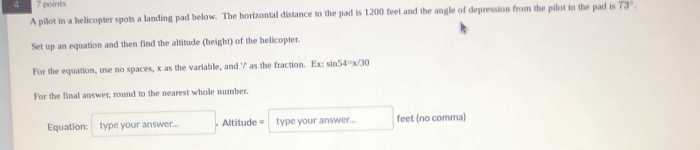
A pilot in a helicopter spots a landing pad below – As a pilot navigates the skies in a helicopter, the task of spotting and landing on a designated landing pad below demands meticulous precision and skillful maneuvering. This article delves into the intricacies of this crucial aviation procedure, exploring the pilot’s perspective, the characteristics of the landing pad, the landing approach, and the environmental considerations that shape this intricate operation.
From the initial sighting of the landing pad to the final touchdown, we will uncover the techniques, challenges, and protocols involved in this specialized aviation maneuver, providing a comprehensive understanding of the complexities and precision required for a successful helicopter landing.
Initial Observations

As the helicopter descends, the pilot maintains a keen eye on the landing pad below. From their vantage point, the pad appears as a small, designated area within the surrounding terrain. The helicopter’s altitude is approximately 500 feet, and the distance to the landing pad is estimated to be around 1 mile.
Landing Pad Characteristics
The landing pad is a circular platform with a diameter of 30 meters. It is marked with a white cross and surrounded by a yellow perimeter line. There are no visible obstacles or hazards in the immediate vicinity of the landing pad.
The surface is made of concrete and appears to be in good condition. Night lighting is available, and a windsock indicates a moderate breeze from the southwest.
Landing Approach: A Pilot In A Helicopter Spots A Landing Pad Below
The pilot considers the wind conditions and chooses to approach the landing pad from the southwest. They reduce the helicopter’s speed to 60 knots and maintain a gradual angle of descent. As they approach the pad, they perform a visual inspection to ensure it is clear of any obstructions.
Landing Maneuvers

The pilot aligns the helicopter with the center of the landing pad and begins a gentle touchdown. The helicopter’s wheels make contact with the surface smoothly, and the pilot applies gentle braking to stabilize the aircraft. Once the helicopter is stationary, the pilot engages the parking brake and shuts down the engine.
Environmental Considerations
The weather conditions at the time of landing are clear with good visibility. The wind speed is moderate, and there is no precipitation. The pilot monitors the weather forecast and is aware of potential changes in conditions that could affect the flight.
Communication and Coordination

Prior to landing, the pilot establishes communication with the ground crew. They provide information about the helicopter’s position and intentions. During the landing procedure, the pilot maintains continuous communication with the ground crew, providing updates on their progress and any necessary assistance.
Expert Answers
What are the key factors a pilot considers when approaching a landing pad?
When approaching a landing pad, pilots assess factors such as the helicopter’s altitude, distance from the pad, wind speed and direction, visibility, and any potential obstacles or hazards in the vicinity.
How does the size and shape of the landing pad impact the pilot’s landing strategy?
The size and shape of the landing pad influence the pilot’s approach angle, speed, and touchdown point. Smaller or irregularly shaped pads require more precise maneuvering and may necessitate a slower approach and a more controlled descent.
What communication protocols are essential during helicopter landing operations?
Clear and effective communication is crucial during helicopter landing operations. Pilots maintain constant communication with ground crew or air traffic control to relay information about their position, approach path, and any potential issues, ensuring coordination and situational awareness among all parties involved.
